Malaria – The Most Common Life-Threatening Disease In India
Malaria, a parasitic disease,which spreads through the bite of an infected mosquito from person to person. It starts as a flu-like disease, and if untreated, gets serious. Parasites of malaria kill red blood cells and cause anemia. The death is caused by injury to the brain or vital organs. Five parasite species cause malaria in humans, and the predominant of them is P. falciparum and P. vivax.
Can Malaria be transmitted by contact?
It doesn’t spread through the air, like cold or flu, and is not transmitted sexually. People owing to casual contact with other infected people, such as seated close to someone who has malaria.
Symptoms
Symptoms are often identical in the initial stages with those of many other diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. It can begin with signs that mimic the flu.
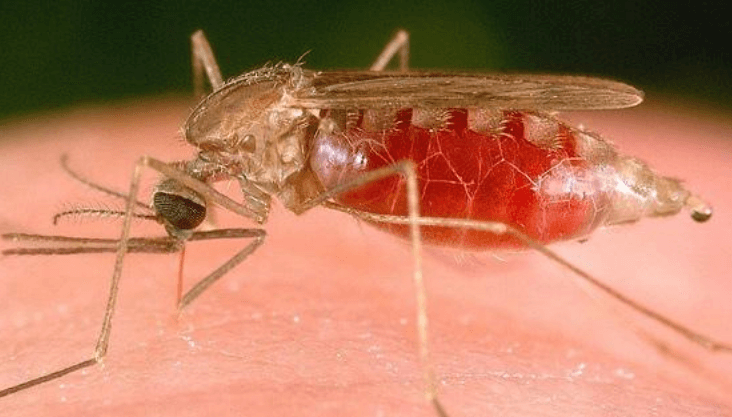
Symptoms can differ based on age, overall health, and the type of malaria parasite you had. The most common symptoms are
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Cerebral malaria
- Headache.
- Sweating
- Drowsiness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Muscle pain.
- Generally feeling sick.
- multiple convulsions
- Cough
- Clinical jaundice and vital essential organ dysfunction
- Chest pain
- Deep breathing and shortness of breath
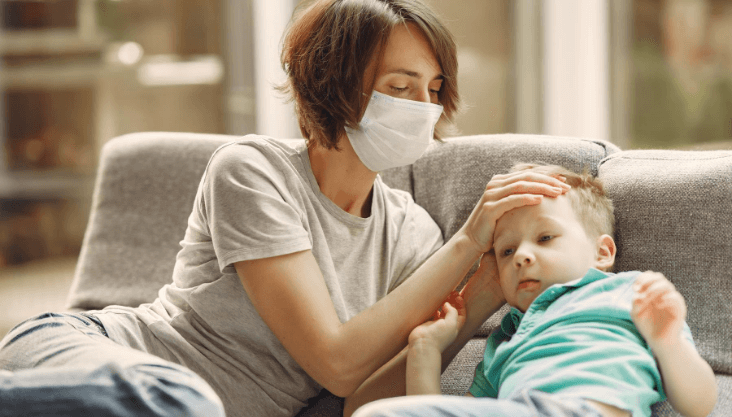

Initial symptoms usually begin in a few weeks when an infected mosquito has bitten them. Several kinds of malaria parasites, nevertheless, can remain dormant in your body for close to a year.
How is Malaria transmitted?
It spreads through the bite of Anopheles female mosquitoes. There are more than 400 distinct Anopheles mosquito species, and 30 are very effective carriers of malaria. This species of mosquitoes bite in the night or early morning. Anopheles mosquitoes lie the eggs in water, which grows into larvae and gradually evolves as mosquitoes. The female mosquitoes are hunting for feed-in blood to protect their eggs. Transfer often relies on climatic factors which can affect mosquito numbers and survival, like cycles of rainfall, temperature, and dampness.
Since malaria-causing parasites impact red blood cells, individuals may also be able to catch malaria from contact with infected blood which includes:
1.From mum to an unborn baby
2.By blood transfusions
3.Sharing the needles used for injecting narcotics
Human immunity is yet another essential factor, particularly for adults in locations with moderate or severe levels of transmission. Partial immunity develops over years of exposure, and although it seldom provides full protection, it lowers the risk of serious illness triggered by malaria infection.
Easy ways to Prevent
- Have an insect spray that contains pyrethroids in all living and sleeping areas, particularly during night and evening hours.
- During evening and nightwear long-sleeve shirts and pants. The less visible skin, the better. Alternatively, permethrin can be used to clean your clothes to keep you safe.
- Verify that the net isn’t broken and always make sure it’s concealed right under your bed. Space should be fitted with nets at doors and windows. Keep the ac on, as mosquitoes prefer to stay out of air-conditioned rooms.
- Pick the correct anti-malarial drugs for the nation you fly to. You will take into consideration your medical record, age, and other related drugs when selecting anti-malarial protection pills. Depending on your choice of drug, take them daily or weekly before travel, upon arrival from the affected zone.
- Children and pregnant women may not fly to areas that are vulnerable to malaria.
Diagnosing Malaria
The doctor will check health records during your visit, including any previous visits to tropical climates. After a physical examination is carried out, the physician will decide whether you have an enlarged spleen or liver. If you have symptoms, physicians will prescribe more blood tests to verify. The test will help to come to the following conclusions.
1.Whether you have malaria ?
2.Which type of malaria you are suffering?
3.If infection caused by a worm immune to other drug products
4.If the disease has caused anemia
5.If the disease has affected your major organs
Blood donation
It varies depending on just what regions you visited in that nation, how long ago you were there, whether you’ve had malaria. In particular, most visitors are withheld from giving blood for 1 year after their return to an area with malaria. People that live in places where malaria is contracted would not be able to donate blood for 3 years. After treatment, people could not give blood for 3 years, during which time they should have remained healthy of malaria symptoms. Blood banks are following specific rules to admit or postpone contributors that were in the malaria-endemic location. They do that now so as not to take blood from an infected donor for transfusions.
Treatment options
Artemisinin-based combination therapies are the initial malaria medication, in several cases. There are various types of ACTs. Sources include artemether-lumefantrine and amodiaquine-artesunate.
Each Artemisinin is a combo of drugs that perform different tasks against the malaria parasite.
The recommended treatment for any drug prone parasite is chloroquine. But the parasites which spread malaria are immune to chloroquine, and the drug is no longer the best medication.
Other drug options available for the treatment are
1.Quinine
2.Atovaquone
3.Proguanil
4.Mefloquine
5.Clindamycin
6.Doxycycline
The patient with falciparum malaria has the most serious symptoms. People with falciparum malaria have to be evaluated in the first weeks of treatment in a facility’s intensive care, as the illness can trigger respiratory failure, coma, and renal failure. Chloroquine is the recommended treatment for pregnant females. Quinine, proguanil, and clindamycin are usually used only for chloroquine-resistant expectant mothers.
Malaria Complications which can prove fatal
1. When blood cells loaded with parasites obstruct tiny blood vessels in the brain, swelling can happen in the brain, or possibly brain damage. Within the cerebrum could even cause seizures and maybe coma.
2. Collected fluid in the lungs, which is often called pulmonary edema can cause breathing problems.
3. It can induce the rupture of your kidneys and liver or the spleen.
The said condition can be life-threatening.
4. It harms the red blood, and this can lead to anemia.
5. Serious types might cause low blood sugar known as
hypoglycemia. Low blood sugar can induce coma or fatality.
Would you like to know more? Connect with our Doctors today.









