Heads up
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It’s common in children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic) and tends to flare periodically. It may be accompanied by asthma or hay fever.
No cure has been found for atopic dermatitis. But treatments and self-care measures can relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks. For example, it helps to avoid harsh soaps, moisturize your skin regularly, and apply medicated creams or ointments. It is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It’s common in children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic) and tends to flare periodically. It may be accompanied by asthma or hay fever. No cure has been found for atopic dermatitis. But treatments and self-care measures can relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks. For example, it helps to avoid harsh soaps, moisturize your skin regularly, and apply medicated creams or ointments.
Symptoms
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) signs and symptoms vary widely from person to person and include:
- Dry skin
- Itching, which may be severe, especially at night
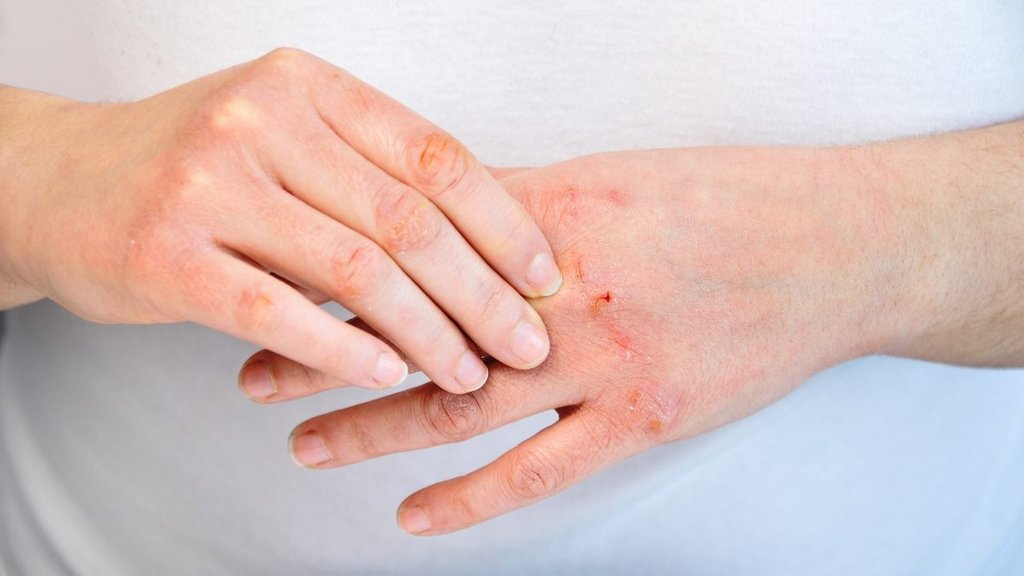
- Red to brownish-gray patches, especially on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees, and in infants, the face and scalp
- Small, raised bumps, which may leak fluid and crust over when scratched
- Thickened, cracked, scaly skin
- Raw, sensitive, swollen skin from scratching
Is eczema and atopic dermatitis the same thing?
Eczema is sometimes called atopic dermatitis, which is the most common form. “Atopic” refers to an allergy. People with eczema often have allergies or asthma along with itchy, red skin. Eczema comes in a few other forms, too
Causes and Risk factors
Causes
- Atopic dermatitis can cause small, red bumps, which can be very itchy.
- When scratched, the bumps may leak fluid and crust over.
- Often occurs where your skin bends inside the elbows, behind the knees and in front of the neck.
- It is related to a gene variation that affects the skin’s ability to provide this protection. This allows your skin to be affected by environmental factors, irritants and allergens.
- In some children, food allergies may play a role in causing eczema.
Risk factors
The primary risk factor for atopic dermatitis is having a personal or family history of eczema, allergies and asthma.
Atopic dermatitis may be triggered or worsened by environmental factors such as:
- Skin irritants, including wool or synthetic clothing, soaps or detergents, cosmetics or perfumes, dust/sand, chemical solvents, chlorine
- Extremes in temperate or climate (cold or hot temperatures or dry air or extremely humid air)
- Lack of moisturizing after bathing
Complications
Complications of atopic dermatitis (eczema) may include:
- Asthma – Eczema sometimes precedes these conditions. More than 60% of young children with atopic dermatitis develop asthma by age 13.
- Chronic itchy, scaly skin – A skin condition called neurodermatitis (lichen simplex chronicus) starts with a patch of itchy skin. You scratch the area, which makes it even itchier. Eventually, you may scratch simply out of habit. This will cause the affected skin to become discolored, thick and leathery.
- Skin infections – Repeated scratching that breaks the skin can cause open sores and cracks.
- Irritant hand – This especially affects people whose work requires that their hands are often wet and exposed to harsh soaps, detergents and disinfectants.
- Allergic contact dermatitis – This condition is common in people with atopic dermatitis.
- Sleep problems. The itch-scratch cycle can cause poor sleep quality.
Prevention
- Moisturize your skin at least twice a day.
- Try to identify and avoid triggers that worsen the condition
- Make sure to have a shortened bath duration
- Taking a bleach bath – A bath with a small amount of bleach added to the water may help lessen symptoms of chronic eczema (atopic dermatitis). Eczema is an itchy skin condition, often worsened by a bacterial infection. An eczema bleach bath can kill bacteria on the skin, reducing itching, redness and scaling.
- Use only gentle soaps
- Dry yourself carefully
When to see a doctor
- Is so uncomfortable that the condition is affecting sleep and daily activities
- Has a skin infection — look for red streaks, pus, yellow scabs
- Continues to experience symptoms despite trying home remedies